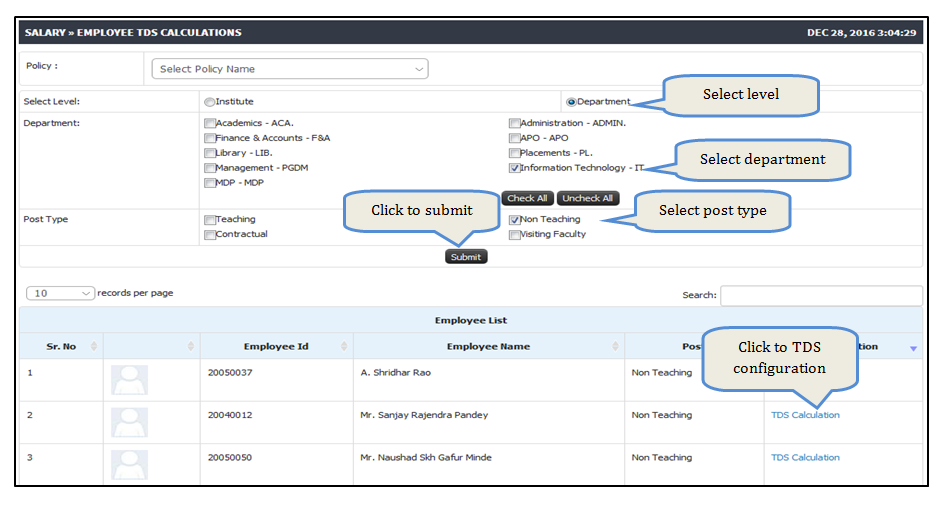
TDS Configuration
TDS Configuration
Under Section 192 of the Income Tax Act, every employer who is paying a salary income to his employee is required to deduct TDS from the salary income if it exceeds the basic exemption limit.
However this configuration can be incorporated in the system so that the TDS for those employees who's salary income exceeds the basic exemption limit is deducted from their gross salary.
Roles
Finance Admin
Path
Finance Admin >> Salary Configuration >> Tax Structure
Inputs Needed
- Defining correct tax slabs as per the declaration in the Union Budget.
- W.E.F (With Effect From) date to be defined correctly.
- Revision of the amounts for tax slabs and exemptions to be studied carefully before the start date of the configured parameter.
Functionality
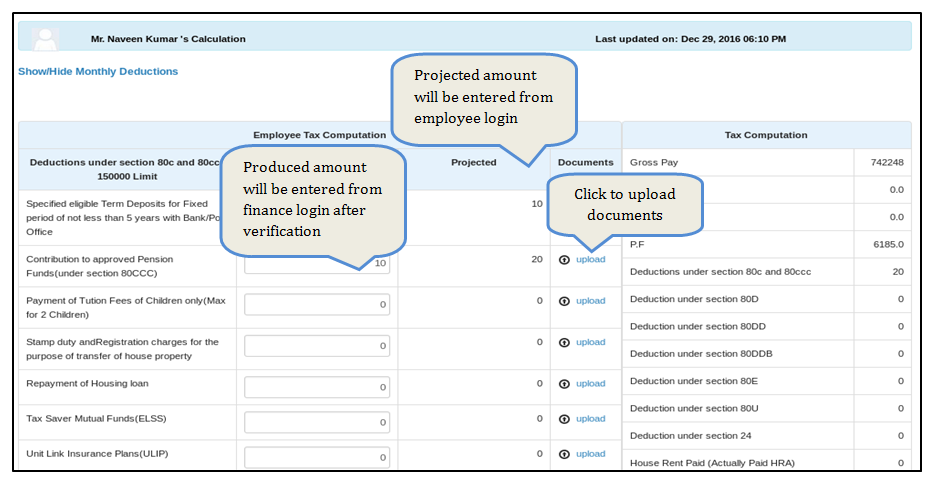
- The employee from his login needs to enter the details about his / her investments in various sectors at the beginning of the Financial Year. The employee also needs to upload the documents if required for the same from their login.
- Once these details are received at the Finance Admin, the Finance Admin can verify the same and depending on the investments, the TDS is calculated through the system which may vary on monthly and annual basis.
- These reflections in the calculations can be viewed at the time of salary calculations of the employees.
1. Tax Slab
- Under the Income Tax Act, 1961 – the percentage of income that is payable as tax to the Government is based on the amount of income that a person has earned during a year.
- Hence for any given financial year the Tax slabs can be configured in the system. The tax slabs can be created individually for Male / Female, Senior Citizen Male / Female, Super Senior Citizen Male / Female employees.
- The system provides the functionality to deduct the TDS (Tax Deduction at Source) on monthly basis. Its is the responsibility of the employee to deposit this amount to the government as TDS for whom the TDS amount has been deducted.
2. Tax Exemptions
- Under this section we can configure multiple parameters through which the Tax Exemptions are defined under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- There are a number of great ways to save taxes. You need to make use of the tax-saving instruments wisely, in order to minimize your tax payments.
- There are several income tax exemptions available under the income tax act and here we will discuss all of the same.
Allowances exempted under Section 10 as per Income Tax Act.
- HRA (House Rent Allowance)
A minimum of the following is the income tax exemption that one gets from HRA: Total HRA received from the employer If rent is less than 10% of the income (Basic salary +Daily Allowance) 40% of the income (Basic + Daily Allowance) and 50% of income (Basic + DA) in metropolitan cities. In such cases, the salary is equal to the basic sum inclusive of the dearness allowance (Basic + DA)
- Allowance on Transportation
The expenditure done in order to commute from your home to work place is unavoidable. However the Government declares a certain amount annually which is exempted under Section 10 of Income Tax Act.
- Children Education Allowance
Children Education is another expenditure which falls under which Tax Exemption is applicable. This benefit can be given by the employers to the employees in order to get Income Tax exemptions. However the limit of this plan is ₹100 per month only for two children.
Exemptions under Section 80 as per Income Tax Act.
1. Section 80D: Medical Insurance Deduction.
2. Section 80DD: Income Tax Exemption for maintenance of Disable Dependent.
3. Section 80DDB: Serious Ailment Deduction
4. Section 80E: Deduction on Loan for Higher Studies.
5. Section 80G: Deductions for donations / charity.
6. Section 80GG: Deduction on House Rent Paid.
7. Section 80TTA: Saving Account Interest Deduction.
8. Section 80U: Deduction for Disabled.
However there are various other Sections and sub-sections under Income Tax Act through which the tax can be exempted.
The system provides the functionality to define each section individually and the configuration for the same will reduce the amount for the TDS deduction from the employee’s salary.
3. Tax Additional Configuration
- A refund on taxes when the liability on tax is less than the tax paid by the individual is referred to as Income Tax Rebate. Taxpayers generally receive a refund on the income tax if they have made payment of tax more than they owe. At the end of the fiscal year, they will receive the refund of tax money.
- The systems provides functionality to define the amount for Tax Rebate which helps the employees to get benefit of refund from Income Tax as per the eligibility criteria.
- Education Cess at 2% was introduced to meet Government’s commitment to provide and finance universalized quality basic education needs of poor people in India as an additional levy on basic tax liability. While this was helping students to complete primary education, Government realized the need for access to secondary and higher education as well and through Finance Act 2007 introduced an additional secondary and higher education cess of 1% to fund secondary and higher education cess. Overall education and secondary higher education cess of 3% was charged on all types of taxes.